Segment and Google Tag Manager (GTM) are two distinct tools utilized for handling and deploying diverse tracking codes and tags on websites. While they share similarities in their basic function, they cater to different objectives and user groups.
What is Segment?
Segment is a platform dedicated to customer data management, collection, and integration. Its core purpose is to centralize customer data from multiple sources and subsequently direct it to diverse destinations, such as analytics platforms, marketing automation tools, data warehouses, and third-party services.
Key Features of Segment include:
Data Collection:
Segment facilitates data collection through SDKs and APIs, enabling you to gather information from your website, mobile apps, and other origins.
Data Integration:
It streamlines data integration by directing it to multiple destinations at once, simplifying the process of connecting various tools and services without requiring separate tracking codes for each.
Data Management:
Segment assists in data management tasks like data cleaning, enrichment, and transformation, ensuring that the data is prepared appropriately before reaching its designated endpoint.
What is Google Tag Manager (GTM)?
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a tag management solution developed by Google. Its primary objective is to simplify the process of implementing and managing different tracking codes (tags) on a website, removing the necessity for manual code adjustments. GTM is widely favored by marketers, analysts, and website owners who want a user-friendly method to incorporate tracking codes for analytics, advertising, and other crucial functionalities.
Key features of Google Tag Manager include:
Tag Deployment:
GTM offers a user-friendly interface that makes it easy to implement tracking codes (tags) on your website without any coding expertise required.
Version Control:
You can effortlessly manage multiple tag versions with GTM, simplifying updates and rollbacks whenever necessary.
Built-in Tags:
GTM comes with a collection of pre-built tags for various services, including Google Analytics, Google Ads, Facebook Pixel, and more, ensuring convenient integration of these essential functionalities into your website.
Read also: Data Filters In Google Analytics 4
Segment Vs. GTM
Key Strength
Segment effortlessly integrates intricate tools, stores comprehensive clickstream data, and facilitates data export to SQL databases. Whereas, GTM facilitates JavaScript loading on webpages and inserts advertising pixels based on rule configurations.
Data Management
Segment excels at storing clickstream data in a consolidated manner, allowing for the replay of historical data in new tools. It offers seamless data export to SQL databases and internal systems. In contrast, Google Tag Manager does not retain data and is incapable of loading historical data into new tools or performing translations for loading historical data into SQL databases.
User Interface
Segment offers a sleek and user-friendly experience, automatically translating data for new tools whenever a destination is enabled. However, Google Tag Manager requires manual configuration of rules and settings for every pixel to fire.
But, Segment’s setup can be more complex, often demanding technical expertise, particularly when dealing with data transformation and routing. In contrast, GTM provides a user-friendly experience and can be easily managed by non-technical users.
Device Compatibility:
Segment supports tracking user events across mobile, web, and server environments. Its server libraries include Python, Ruby, Node, Java, PHP, Clojure, Rust, .NET, Go, and Xamarin.
On the other hand, Tag Manager primarily operates on the web and has limited functionality on mobile devices. It does not offer support for server destinations.
Use Case:
Segment is well-suited for businesses requiring the collection and management of customer data from diverse sources, with the capability to route it to multiple destinations. It serves as a robust tool for data integration and analytics. Conversely, Google Tag Manager is specifically designed for the management of tracking codes, making it an ideal choice for website owners seeking a straightforward method to implement and organize tags.
Should I integrate GTM into Segment, or Segment into GTM?
Both options are possible. You have the flexibility to install the GTM into Segment or integrate Segment into the GTM. In certain cases, businesses may choose to utilize both tools together. For instance, they can employ Segment to collect and manage customer data from diverse sources, and then utilize Google Tag Manager to deploy specific tags on the website for tracking and analytics functionalities.
GTM in Segment
Segment recommends the installation of GTM within its framework. This integration allows Segment to transmit the similar event data into different data sources within their respective formats.
For instance, when a user clicks on the ‘add to cart’ button, Segment can seamlessly send this data to various analytics platforms such as Google Analytics, Kissmetric, Piwik, Adobe Analytics, and more. In the context of Segment, GTM functions as just another data source that contributes to its comprehensive data management capabilities.
Segment in GTM
For Google Tag Manager (GTM), Segment is treated as another tag. Installing Segment via GTM may lead to difficulties in routing and translating data in a format that GTM and other sources of data can comprehend. In some cases, this integration might not work at all.
Therefore, it is advisable to avoid installing Segments via GTM to ensure smooth and efficient data handling without potential compatibility issues.
Installing the GTM into Segment.com
Follow the easy steps outlined below:
Sign up for the account at Segment.com. However, you can start with the free developer account to explore the features and functionality of Segment.
Step 2:
Choose your initial data source. For now, select ‘Website’ as the data source.

Step 3:
Put your website name and URL. Copy the generated code snippet and paste a Segment snippet into a head section on each page of your website:

Step 4:
Verify the record of Events on Segment by clicking on a ‘Debugger’ link at the top navigation.
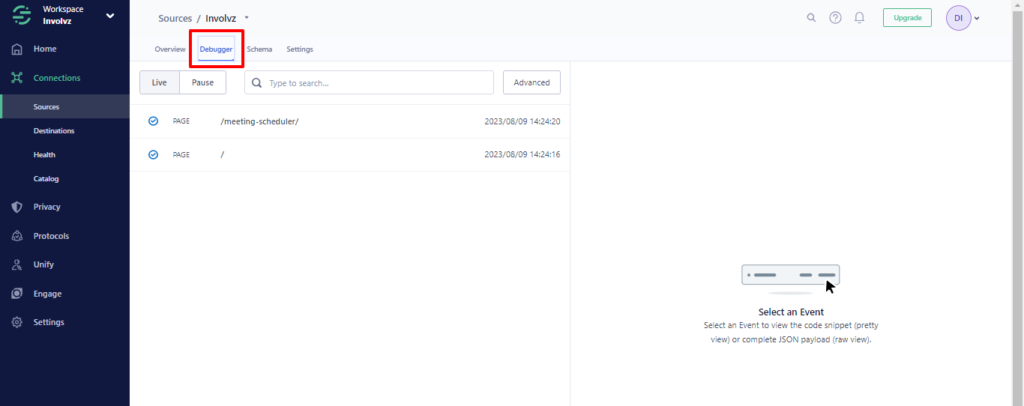
If a ‘segment’ is successfully recording the events, you will be able to view event data, confirming that Segment is installed correctly in your website.
Step 5:
Access your Google Tag Manager account and take note of a container ID.
Step 6:
Return to Segment account and click upon ‘Destination’ link below the source Link.

Step 7:
In destination Tab you need to click on ‘Add Destination’ Button. After clicking the button you will redirected to Catalogue Tab. In Catalogue tab locate and select the ‘Google Tag Manager’ setup.

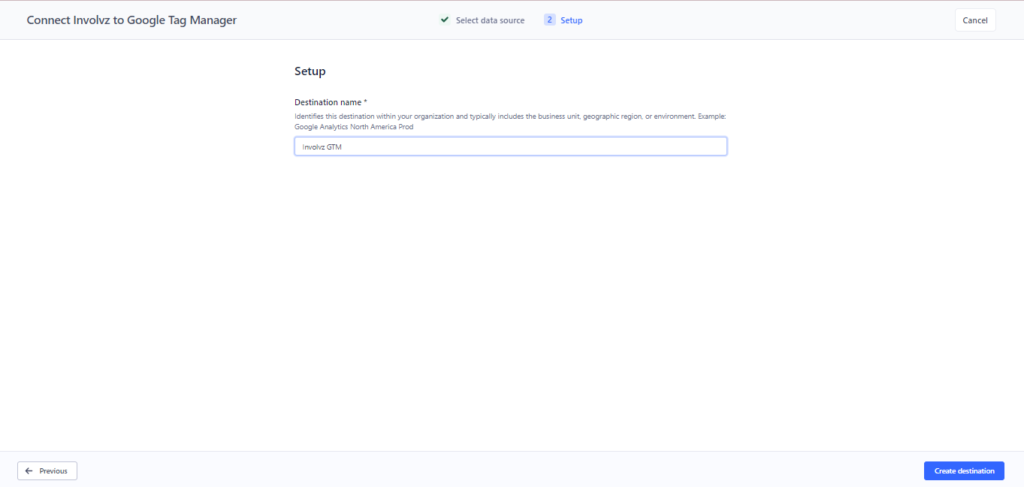
Step 8:
Input the ‘Destination Name’ and proceed by clicking upon ‘Create Destination’.
Step 9:
Eliminate the Google Tag Manager container tag code from every page of a website.
Note (1): After implementing GTM into the Segment, Google Tag Assistant will no longer function as it will not be capable of locating a container code embedded in the webpage.
Note (2): If you are using Google Analytics through GTM, avoid activating the Google Analytics integration into the Segment.
Step 10: Proceed to utilize GTM as usual, but now you won’t need to hard code data layers in your website.
Instead, you’ll track events through Segment, & Segment will automatically translate these tracked events in a data layer, making them accessible via GTM. This approach allows you to send the similar events to the different data sources, not limited to just GTM.
Read our latest published articles about Understanding Event Parameter in Google Analytics 4